Difference between revisions of "Spin Orbit Coupling"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
===Square lattice=== | ===Square lattice=== | ||
The experimental realization is published here <ref>PRL 121, 150401 (2018)</ref>. 2 orthogonal beams are sent back and forth to create a square lattice: | The experimental realization is published here <ref>PRL 121, 150401 (2018)</ref>. 2 orthogonal beams are sent back and forth to create a square lattice: | ||
| − | <math>V_{latt}=V_0\cos^2(k_0 x)+V_0\sin^2(k_0 y)</math>. The total Hamiltonian of the system reads as <math>\hat H = \frac{p^2}{2m}+V_{latt}+\Omega_{R}(x,y)+\frac{\delta}{2}\sigma_z</math> | + | <math>V_{latt}=V_0\cos^2(k_0 x)+V_0\sin^2(k_0 y)</math>. The total Hamiltonian of the system reads as <math>\hat H = \frac{p^2}{2m}+V_{latt}+\Omega_{R}(x,y)+\frac{\delta}{2}\sigma_z</math>, where δ is the two-photon detuning. By tuning the phase between two beams δφ it is possible to transition from 1D to 2D SOC. For phases δφ=0, π, they demonsrate 1D SOC. For phases δφ=±π/2 they have symmetrical 2D SOC. |
| − | <ref> </ref> | + | <ref> </ref>. |
<math></math> | <math></math> | ||
| + | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
[[Category:BEC]] | [[Category:BEC]] | ||
Revision as of 14:06, 3 February 2020
Creation of 2D SOC
Square lattice
The experimental realization is published here [1]. 2 orthogonal beams are sent back and forth to create a square lattice:
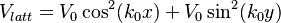 . The total Hamiltonian of the system reads as
. The total Hamiltonian of the system reads as 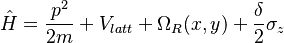 , where δ is the two-photon detuning. By tuning the phase between two beams δφ it is possible to transition from 1D to 2D SOC. For phases δφ=0, π, they demonsrate 1D SOC. For phases δφ=±π/2 they have symmetrical 2D SOC.
[2].
, where δ is the two-photon detuning. By tuning the phase between two beams δφ it is possible to transition from 1D to 2D SOC. For phases δφ=0, π, they demonsrate 1D SOC. For phases δφ=±π/2 they have symmetrical 2D SOC.
[2].