Photodetectors
Revision as of 21:26, 18 November 2018 by imported>Kot (→Quantum efficiency)
Contents
Quantum efficiency
The quantum efficiency is defined as fraction of incident photons which are absorbed by photoconductor and generated electrons which are collected at the detector terminal.
Practical formula for quantum efficiency can be derived from responsivity on a given wavelength:
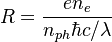 Thus
Thus
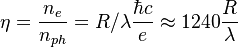 , where responsivity is given in Amperes per Watt (A/W), while wavelength is in nanometers (nm).
, where responsivity is given in Amperes per Watt (A/W), while wavelength is in nanometers (nm).
Detectors by wavelenght
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
The different detectors are used depending on a wavelength of interest
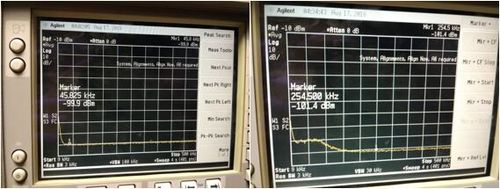
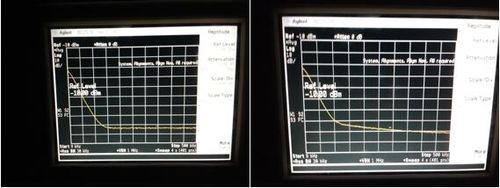
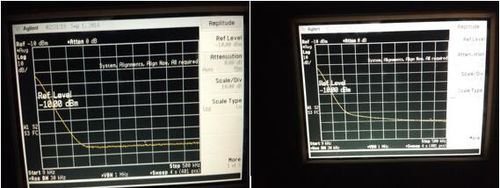
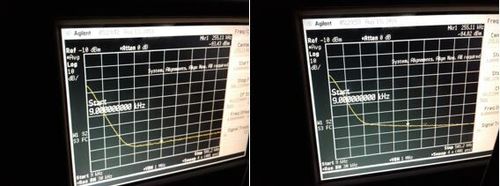
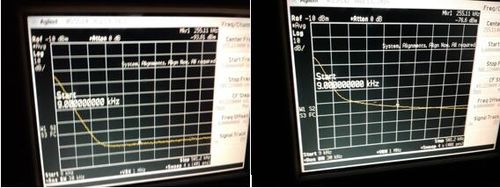
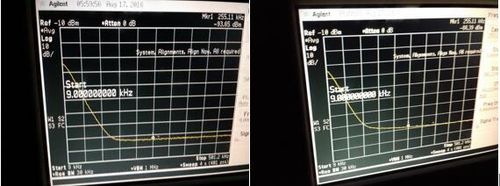
Slow photodetectors
Characteristics:
| Photodetector, # | Estimated Bandwidth (kHz) | Responsivity (mV/µW) | Saturation Power (µW) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 23 | 1.97 | N/A |
| 2 | 23 | 445 | 34.9 |
| 3 | 23 | 460.8 | 31.9 |
| 4 | 23 | 8.96 | N/A |
| 5 | 23 | 11.79 | N/A |
| 6 | 58 | 1.44 | N/A |