Detectors- Kazan
Improvements:
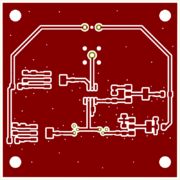
- larger ground holes(viases)
- PD case to ground
- small capacitors to 1206 case
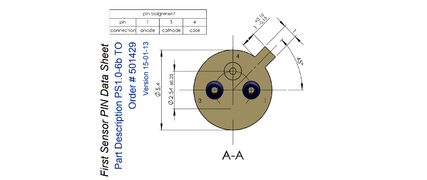
- label cathode and anode
- change pin order
- distance between holes for screws is unequal (54.11mm and 52.94mm)
- change photodetector holder to have hole and post
- DIS pin is shorted to gnd, should be high
- It oscillates, has offset (due to mismatch between R8 and R10), wide electronic noise
- Make sure, that R8 and R10 are matched well.
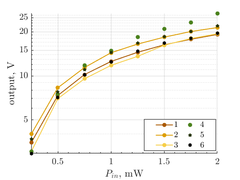
lambda=630nm HeNe (orange)
| PWR [mW], mV
|
#1
|
#2
|
#3
|
#4
|
#5
|
#6
|
| 2
|
19.2
|
21.4
|
19.4
|
26.8
|
19.6
|
22
|
| 1.75
|
19.2
|
21.4
|
19.4
|
23.2
|
19.6
|
22
|
| 1.5
|
16.3
|
18.4
|
16.2
|
21
|
16.8
|
18.6
|
| 1.25
|
14.5
|
16.5
|
13.6
|
18.4
|
14.7
|
16.8
|
| 1
|
12.55
|
14.4
|
11.8
|
14.8
|
12.5
|
14.5
|
| 0.75
|
10.2
|
11.4
|
9.55
|
11.8
|
10.2
|
11
|
| 0.5
|
7.35
|
8.3
|
7
|
7.5
|
7.1
|
7.76
|
| 0.25
|
3.5
|
4
|
3.04
|
3.05
|
2.95
|
3.7
|
lambda=606nm Dye (black)
| PWR [mW],
|
#1
|
#2
|
| 5
|
3.5
|
|
| 4.5
|
3.5
|
|
| 4
|
3.5
|
-3.22
|
| 3.
|
3.5
|
-3.22
|
| 2
|
3.4
|
-3.24
|
| 1.5
|
2.5
|
-2.55
|
| 1
|
1.75
|
1.76
|
| 0.75
|
1.26
|
-1.26
|
| 0.5
|
0.85
|
-0.84
|
| 0.25
|
0.43
|
-0.4
|
Photodiodes comparison
| Diode
|
Responsivity
|
Active area
|
Dark current
|
Capacitance
|
Rise time
|
| PS1.0-6b TO
|
0.43 A/W (@ 606 nm)
|
1 mm2
|
0.05 nA
|
5-20 pF
|
10-30 ns
|
| Hamamatsu
|
0.39 A/W (@ 606 nm)
|
1.1 mm2
|
0.07 nA
|
3 pF
|
The detector is photodiode First Sensor PS1.0-6B Photodetectors manufacturer First Sensor, part number PS1.0-6B-TO52S1.3.
The detector used in original homodyne by Hamamatsu: S5972
Shot noise and thermal noise
Shot noise accompanies a flow of electric current. Any resistor at any given temperature emits thermal noise. Amplification is a nonequilibrium process, and thus amplification involves noise sources other than thermal sources.[1]
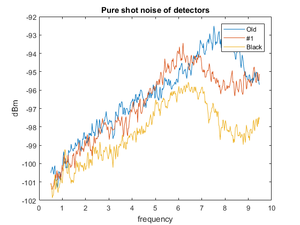
Levels of electronic shot noise for three homodyne detectors. Homodyne #1, produced by Ed ~2014-2015.
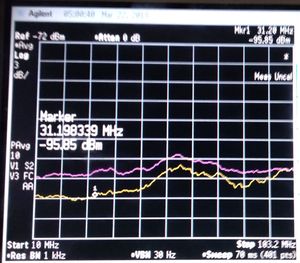
Homodyne #1, produced by Ed ~2014-2015. Shot noise levels without signal channel( pink trace), with signal applied 115MHz yellow trace, (? 15 uW)

Homodyne black, produced in Moscow 2017. Shot noise levels without signal channel( yellow trace), with signal applied with power 15 uW, and frequency 80 MHzwith respect to LO (blue trace)
Homodyne schematic
[2]
[3]
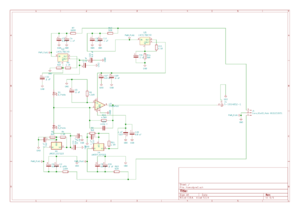
Homemade homodyne schematics
Heterodyne detection
Main aspects of homodyne detection.
References
- ↑ Hermann Haus, Electromagnetic noise and quantum optical measurements, (/Cold Atoms/Books)
- ↑ Hermann Haus, Electromagnetic noise ans quantum optical measurements, (New York: Academic Press, 2005), 23-5.
- ↑ Hermann Haus, Electromagnetic noise ans quantum optical measurements, (New York: Academic Press, 2005), 23-5.