Magnetometry
BEC
Spin-echo-based magnetometry with spinor Bose-Einstein condensates
Abstract. In this work they have noticed that magnetic field created by ac line disrupts their experiments, by applying a magnetic field with an opposite phase they reduce the noise to 1 nT. As a magnetometer they achieved 12 pT/sqrt(Hz) with spatial resolution 100 um^2. For the experiment they average over 10 points.
Technicalities. For the coils they use low ripple current source <2uA (Newport 505), they insert permalloy plates into the room walls. The BEC of 87Rb is prepared in a crossed far-off resonant optical trap (FORT with waxial=30 Hz, wrad=100 Hz), 5*103 atoms are prepared in F=2.
Idea. The rf Hahn-echo pulse sequence is sent: 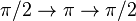 If there is an external varying magnetic field the phase measured in this experiment is:
If there is an external varying magnetic field the phase measured in this experiment is: ![\theta = \frac{g_F \mu_B}{\hbar} \left[ \int_0^{\tau/2}b(t)dt- \int_{\tau/2}^{\tau}b(t)dt \right]](/images/math/9/d/a/9da94c7c984023e556b7a26afbf0b67a.png) . The sensitivity of the magnetometer for a single measurement is given by:
. The sensitivity of the magnetometer for a single measurement is given by:
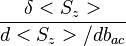 , where
, where 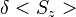 is uncertainty of a single measurement.
is uncertainty of a single measurement.
One more trick to raise the accuracy is to spatially separate atoms with different mF values, thus to obtain all of them in one measurement.