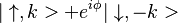Difference between revisions of "Topology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
===Direct measurement of the Zak phase in topological Bloch bands=== | ===Direct measurement of the Zak phase in topological Bloch bands=== | ||
They work with 1D dimerized optical lattice (or as they call it a superlattice), which leads to the Rice-Mele Hamiltonian: | They work with 1D dimerized optical lattice (or as they call it a superlattice), which leads to the Rice-Mele Hamiltonian: | ||
| − | <math>\bar H = -\sum_n(Ja^\dagger_n b_n+J'a^\dagger b_{n-1}+\text{h.c.})+\Delta\sum_n(a^\dagger_n a_n-b^\dagger_n b_n)</math>. If Δ is tuned to be equal then the system corresponds to the Su-Schrieffer-Heeger (SSH) model, which has two topologically distinct phases. The Zak phase difference between them is equal to π. | + | <math>\bar H = -\sum_n(Ja^\dagger_n b_n+J'a^\dagger b_{n-1}+\text{h.c.})+\Delta\sum_n(a^\dagger_n a_n-b^\dagger_n b_n)</math>. If Δ is tuned to be equal then the system corresponds to the Su-Schrieffer-Heeger (SSH) model, which has two topologically distinct phases. The Zak phase difference between them is equal to π. The Zak phase is a gauge dependent quality, although the Zak phase difference of the two dimerizations is uniquely defined. Total phase obtained by a particle moved through the Brillouin zone has three contributions: geometric phase (Zak), dynamical phase (<math>\int{H dt}</math>), and a phase due to Zeeman energy. |
| + | '''Experimental procedure''' | ||
| + | * By conrolling phase between two standing-wave lasers they were able to tune across phase transition. | ||
| + | # prepare atoms in |↓, k=0> state | ||
| + | # apply a π/2 pulse to have a superposition of ↑ and ↓, | ||
| + | # the force created by the magnetic field acts in opposite directions, thus superposition evolves into <math>|\uparrow,k>+e^{i\phi}|\downarrow,-k></math> | ||
| + | |||
<gallery mode="packed-hover"> | <gallery mode="packed-hover"> | ||
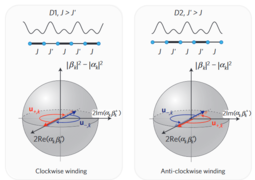
File:Berry 20200224 1.PNG | Two phases | File:Berry 20200224 1.PNG | Two phases | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
[[Category:BEC]] | [[Category:BEC]] | ||
Revision as of 14:51, 25 February 2020
Spielman's review.
Berry phase
Direct measurement of the Zak phase in topological Bloch bands
They work with 1D dimerized optical lattice (or as they call it a superlattice), which leads to the Rice-Mele Hamiltonian:
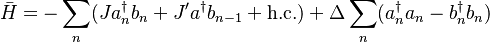 . If Δ is tuned to be equal then the system corresponds to the Su-Schrieffer-Heeger (SSH) model, which has two topologically distinct phases. The Zak phase difference between them is equal to π. The Zak phase is a gauge dependent quality, although the Zak phase difference of the two dimerizations is uniquely defined. Total phase obtained by a particle moved through the Brillouin zone has three contributions: geometric phase (Zak), dynamical phase (
. If Δ is tuned to be equal then the system corresponds to the Su-Schrieffer-Heeger (SSH) model, which has two topologically distinct phases. The Zak phase difference between them is equal to π. The Zak phase is a gauge dependent quality, although the Zak phase difference of the two dimerizations is uniquely defined. Total phase obtained by a particle moved through the Brillouin zone has three contributions: geometric phase (Zak), dynamical phase (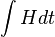 ), and a phase due to Zeeman energy.
Experimental procedure
), and a phase due to Zeeman energy.
Experimental procedure
- By conrolling phase between two standing-wave lasers they were able to tune across phase transition.
- prepare atoms in |↓, k=0> state
- apply a π/2 pulse to have a superposition of ↑ and ↓,
- the force created by the magnetic field acts in opposite directions, thus superposition evolves into