Difference between revisions of "Homodyne"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
imported>Kot |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | ==Detectors- Kazan== | ||
| + | [https://eu.mouser.com/ProductDetail/First-Sensor/PS10-6B-TO52S13?qs=hIohqi1S7IpnxK5X5xc9dg== Photodetectors] | ||
| + | [[Category:Praseodymium]] | ||
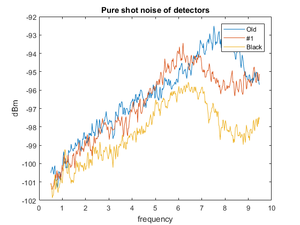
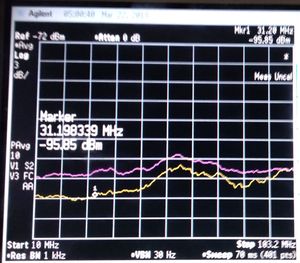
==Shot noise and thermal noise== | ==Shot noise and thermal noise== | ||
Shot noise accompanies a flow of electric current. Any resistor at any given temperature emits thermal noise. Amplification is a nonequilibrium process, and thus amplification involves noise sources other than thermal sources.<ref>Hermann Haus, ''Electromagnetic noise and quantum optical measurements'', (/Cold Atoms/Books)</ref> | Shot noise accompanies a flow of electric current. Any resistor at any given temperature emits thermal noise. Amplification is a nonequilibrium process, and thus amplification involves noise sources other than thermal sources.<ref>Hermann Haus, ''Electromagnetic noise and quantum optical measurements'', (/Cold Atoms/Books)</ref> | ||
Revision as of 09:17, 7 October 2019
Contents
Detectors- Kazan
Shot noise and thermal noise
Shot noise accompanies a flow of electric current. Any resistor at any given temperature emits thermal noise. Amplification is a nonequilibrium process, and thus amplification involves noise sources other than thermal sources.[1]
Homodyne schematic
Heterodyne detection
Main aspects of homodyne detection.
References
- ↑ Hermann Haus, Electromagnetic noise and quantum optical measurements, (/Cold Atoms/Books)
- ↑ Hermann Haus, Electromagnetic noise ans quantum optical measurements, (New York: Academic Press, 2005), 23-5.
- ↑ Hermann Haus, Electromagnetic noise ans quantum optical measurements, (New York: Academic Press, 2005), 23-5.