Difference between revisions of "Homodyne"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
* small capacitors to 1206 case | * small capacitors to 1206 case | ||
* label cathode and anode | * label cathode and anode | ||
| + | * change pin order | ||
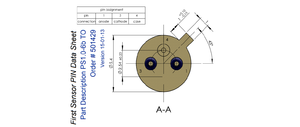
[[File:Homo PD scheme 71019.png|300px|thumb|left|Pins]] | [[File:Homo PD scheme 71019.png|300px|thumb|left|Pins]] | ||
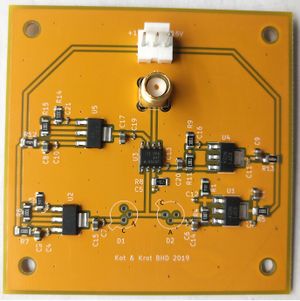
[[File:Homo1 photo 20190824.jpg|300px|thumb|left|Pins]] | [[File:Homo1 photo 20190824.jpg|300px|thumb|left|Pins]] | ||
Revision as of 10:20, 7 October 2019
Contents
Detectors- Kazan
Improvements:
- larger ground holes(viases)
- PD case to ground
- small capacitors to 1206 case
- label cathode and anode
- change pin order
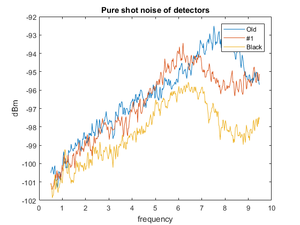
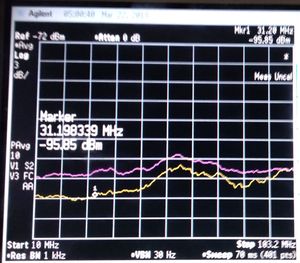
Shot noise and thermal noise
Shot noise accompanies a flow of electric current. Any resistor at any given temperature emits thermal noise. Amplification is a nonequilibrium process, and thus amplification involves noise sources other than thermal sources.[1]
Homodyne schematic
Heterodyne detection
Main aspects of homodyne detection.
References
- ↑ Hermann Haus, Electromagnetic noise and quantum optical measurements, (/Cold Atoms/Books)
- ↑ Hermann Haus, Electromagnetic noise ans quantum optical measurements, (New York: Academic Press, 2005), 23-5.
- ↑ Hermann Haus, Electromagnetic noise ans quantum optical measurements, (New York: Academic Press, 2005), 23-5.