EOM
EOM Kazan
Company Qubig produces eom PS3D-BC
| Parameter | MIN | TYP | MAX | units |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth | DC | 200 | MHz | |
| Maximum voltage | 500 | V | ||

|
1 | kV |
EOM Calgary
We bought a 10 GHZ phase modulator NIR-MPX80 from iX-Blue. The material is lithium niobate, characteristics are
| Parameter | MIN | TYP | MAX | units |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | 780 | 850 | 890 | nm |
| Insertion loss | 3.5 | 4.5 | dB | |
| Electro-optic bandwidth | 10 | 12 | GHz | |
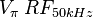
|
4 | 5 | V |
Absolute maximum ratings:
| Parameter | MAX | units |
|---|---|---|
| RF input power | 28 | dBm |
| Optical input power | 14 | dBm |
How to find modulation depth from these parameters?
Let's assume we apply the optical wave with frequency 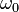 and amplitude
and amplitude 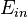 and modulate the EO crystal with RF frequency
and modulate the EO crystal with RF frequency 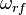 The output of EOM is described by the following expression:
The output of EOM is described by the following expression:
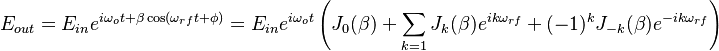
Thus the maximum intensity of the first sideband is reached at 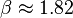 ,
,
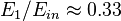 .
.
Thus by varying applied rf power and finding maximum it is possible to translate it into modulation depth index.